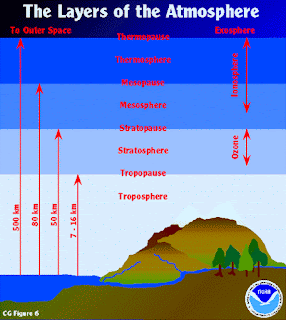
The area near the surface of the earth can be divided up into four inter-connected "geo-spheres:" the lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere. Scientists can classify life and material on or near the surface of the earth to be in any of these four spheres.
NASA Goddard manages the TIMED mission for the Heliophysics Division within the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, built the spacecraft for NASA.
NASA Goddard manages the TIMED mission for the Heliophysics Division within the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland, built the spacecraft for NASA.
 |
Credits: Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía |
NASA’s TIMED mission, short for Thermosphere, Ionosphere, Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics, has confirmed a surprisingly fast carbon dioxide increase in Earth’s upper atmosphere, raising questions about how different layers of the atmosphere are interconnected. Even more curious—though climate models predict carbon dioxide should increase more or less equally across the globe, in its 14 years of data collection, TIMED data revealed that the carbon dioxide in these upper layers, long thought to follow the same patterns across the globe, is increasing faster over the Northern Hemisphere.Though the Northern Hemisphere produces much more carbon dioxide because of its greater land area and population, scientists expect the difference to become negligible at such great heights due to diffusion and mixing.
Understanding the way carbon dioxide moves throughout the atmosphere is key, both for making accurate climate models and for planning spacecraft flight paths. Though carbon dioxide raises temperatures near Earth’s surface, it actually causes cooling in the upper atmosphere, reducing air density in these outermost reaches of the atmosphere and impacting spacecraft orbits.“We tend to separate them into different fields—lower atmosphere is Earth science, upper atmosphere is heliophysics—but we need to understand the atmosphere as a complete system.”
Before TIMED, the only measurements of carbon dioxide in the upper atmosphere were direct measurements from sounding rocket research flights and short-lived spaceborne sensors.
FRIENDS!!!
Though carbon dioxide raises temperatures near Earth’s surface, it actually causes cooling in the upper atmosphere, reducing air density in these outermost reaches of the atmosphere and impacting spacecraft orbits.NASA’s TIMED mission has confirmed a surprisingly fast carbon dioxide increase in Earth’s upper atmosphere using 14 years of data from a radiometer aboard the satellite.
http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard
http://geography.about.com/od/physicalgeography
https://www.google.com.sa




No comments:
Post a Comment